Sustainable and Regenerative Agriculture and Its Impact on the Food Industry
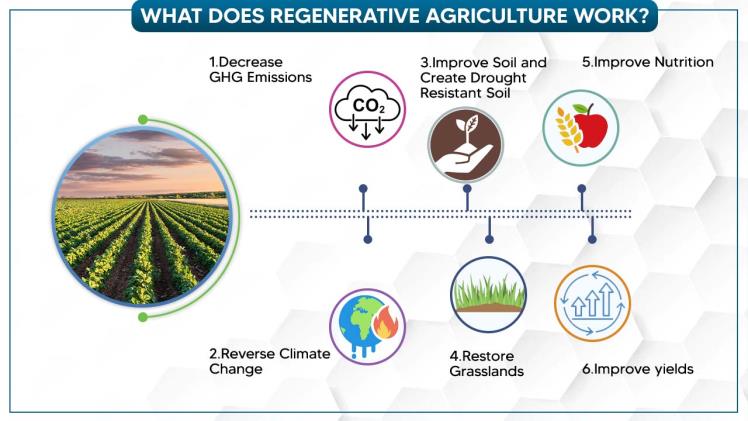
Sustainability and regenerative agriculture are increasingly seen as essential tools in combatting climate change and protecting Earth’s health. These approaches reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming operations, improve farm resilience to changing conditions, and enhance soil and water quality at the same time.
1. Food Security
The global food supply chain is comprised of many stakeholders, from individual households to large industrial farms. Its success depends on ensuring there is enough and quality food supply in response to rising demand as well as market volatility, pest or disease outbreaks and market volatility. We can increase our food systems’ resilience through increasing biodiversity and crop diversity by encouraging more small farmers to join in the mix.
2. Soil Quality
Soil quality is fundamental for food production sustainability, and regenerative practices can improve it rapidly. Farmers can achieve this by reducing or eliminating chemical inputs, improving crop rotation, incorporating compost into their farming and agroforestry practices, as well as protecting the ground from pests, diseases and extreme weather events. The advantages of these practices include improved yields, lower costs and greater resilience to weather events as well as market volatility.
3. Healthy Soils and Ecosystems
Soils provide essential nourishment to plants, animals, and microbes in our ecosystems. That’s why regenerative agricultural practices strive to preserve and build up our soils through avoiding tillage, covering fields with mulch all year round, keeping fields free of chemicals, and diversifying crop types. Doing this prevents soils from being depleted of essential nutrients which in turn provides a healthier habitat for beneficial fungi, bacteria, worms, annelids, nematodes and microbes that feed off these same nutrients.
4. Farm Workers and Animals
Regenerative farmers prioritize labor considerations such as increased pay and benefits for their employees, limiting work hours, and treating farm workers with respect and dignity. Furthermore, they encourage their staff to take regular breaks to enjoy a high quality of life.
5. Biodiversity and Soil Health
Regenerative agricultural practices consider the soil to be a living system, where plants, fungi, ants and other organisms all interact. Soil health is essential for sequestering carbon which is vital for our planet’s sustainability. Furthermore, healthy soil can retain more water, support higher crop yields and sequester more carbon than soil that has been damaged by chemical fertilizers or pesticides.
6. Crop Diversity and Income Potential
Crop diversification can have a substantial financial benefit, particularly in the short run. Not only does it protect cash crops from market price volatility, but also diseases and pests that threaten them. Furthermore, species diversity helps increase food nutritional value as well as improves its production quality across an ecosystem.
Regenerative agriculture offers immense potential economic and social advantages, yet it has yet to gain widespread acceptance. Nonetheless, a movement is growing to promote this approach with many organizations striving to certify or identify regenerative producers and market their products.